In the midst of the bustling activity that defines our kitchens, a seemingly innocent practice persists, one that could be laying the groundwork for a plumbing catastrophe beneath our feet. The act of pouring grease down the drain, often dismissed as harmless or quickly remedied with hot water, is a widespread habit with hidden repercussions. This seemingly benign liquid, a byproduct of our daily cooking, undergoes a dramatic transformation once it descends into the cool confines of home plumbing systems, setting the stage for blockages that can have far-reaching consequences.

The journey from liquid to blockage is not immediate but is a gradual process that betrays the immediate convenience of disposing of fats, oils, and greases (FOGs) down our kitchen sinks. Unbeknownst to many, the grease that flows easily in the warmth of a pan solidifies upon meeting the cold surfaces of underground pipes, clinging tenaciously to their walls and accumulating over time. This article delves into the science behind grease solidification, the myths surrounding hot water as a preventive measure, and the tangible impacts these blockages can have on homes, municipal sewer systems, and the environment.
Understanding the hidden dangers of this all-too-common practice is the first step in preventing the costly and unpleasant consequences that can arise from a blocked plumbing system. As we explore the journey of grease from a hot frying pan to a solid mass within our drains, we invite readers to reconsider how they dispose of kitchen waste and to adopt practices that protect their homes and their community’s infrastructure.
The Science Behind Grease Solidification
When hot grease is poured down the kitchen sink, it embarks on a journey that transforms it from a liquid to a formidable adversary against plumbing health. This transformation is governed by simple science: fats, oils, and greases (FOGs) are liquid at the temperature of cooking but begin to solidify as they cool. The plumbing system of a home provides an ideal environment for this solidification process, with the temperature in the pipes being significantly cooler than in the heated environment of a kitchen.
Upon entering the plumbing system, the warm grease encounters the cooler temperatures of the pipes. These pipes, often just a few feet underground, maintain a consistent cool temperature due to the surrounding soil, regardless of the weather above ground. Contrary to common belief, even hot water poured down the drain does little to alter this cool environment. As the grease cools, it transitions from a liquid to a semi-solid state, adhering to the pipe walls. Over time, this grease builds up, layer by layer, reducing the effective diameter of the pipes and significantly hindering water flow.
This buildup doesn’t occur overnight but results from repeated disposals of grease down the drain. Each addition contributes to the layering effect, much like the rings of a tree, each telling the story of a meal prepared and disposed of without a second thought. The cumulative effect of this disposal method is a plumbing system burdened with hardened grease, leading to reduced efficiency and, ultimately, blockage.
Understanding the science behind grease solidification is crucial for homeowners. It not only demystifies the process but also highlights the importance of mindful disposal of kitchen waste. By recognizing the role of temperature in the fate of disposed grease, individuals can make informed decisions about waste disposal, opting for alternatives that protect their home’s plumbing and, by extension, the broader municipal sewer system from the unintended consequences of grease blockages.
Immediate and Long-Term Consequences of Grease Blockages
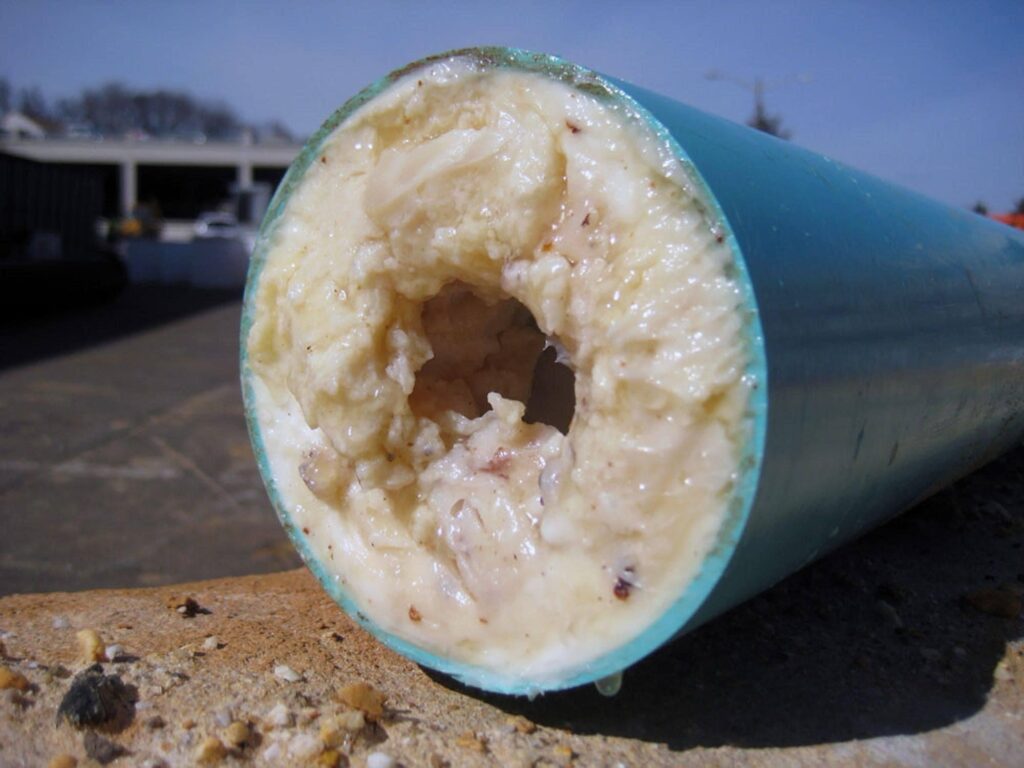

The seemingly innocuous act of pouring grease down the drain can lead to a cascade of plumbing problems, ranging from minor inconveniences to significant household disasters. Understanding both the immediate and long-term consequences of grease blockages can illuminate the extent of potential damage and the importance of proper disposal practices.
Immediate Consequences: Slow Drainage and Clogs
Initially, the buildup of grease in the pipes may not be noticeable. Over time, however, homeowners may begin to observe slower drainage in sinks and other fixtures. This is often the first sign of a developing problem within the plumbing system. As grease continues to accumulate, it can lead to partial or complete clogs, disrupting the flow of wastewater from the home. These blockages can cause water to back up in sinks, showers, and toilets, presenting not only a nuisance but also a hygiene concern.
Long-Term Impacts: Sewage Backups and Environmental Hazards
The long-term consequences of grease accumulation can be far more severe. In extreme cases, blockages can lead to sewage backups, where wastewater flows back into the home instead of out to the municipal sewer system. This situation poses significant health risks, as sewage can contain harmful bacteria and other pathogens. Furthermore, the cleanup and repair involved in addressing a sewage backup are both costly and disruptive.
On a larger scale, grease blockages in the home can extend to municipal sewer lines, affecting entire neighborhoods or communities. When grease makes its way into the public sewer system, it can solidify and attach to sewer pipes, reducing capacity and causing widespread blockages. These issues strain municipal resources, leading to expensive maintenance and repair efforts. Additionally, severe blockages in the sewer system can result in untreated sewage being released into the environment, polluting waterways and harming local ecosystems.

Prevention: A Key to Avoiding Consequences
The immediate and long-term consequences of grease blockages highlight the critical need for preventive measures. Homeowners play a vital role in this effort by adopting simple yet effective disposal practices, such as allowing grease to cool and solidify before scraping it into the trash. By taking proactive steps to minimize grease disposal down the drain, individuals can protect their home’s plumbing, contribute to the health of their community’s sewer system, and reduce the environmental impact of grease-related pollution.
Understanding the repercussions of grease blockages not only in one’s home but also in the broader community underscores the importance of responsible kitchen waste management. As we move towards more sustainable practices, recognizing the power of prevention can lead to significant improvements in our shared infrastructure and natural environment.
The Myth of Hot Water as a Solution
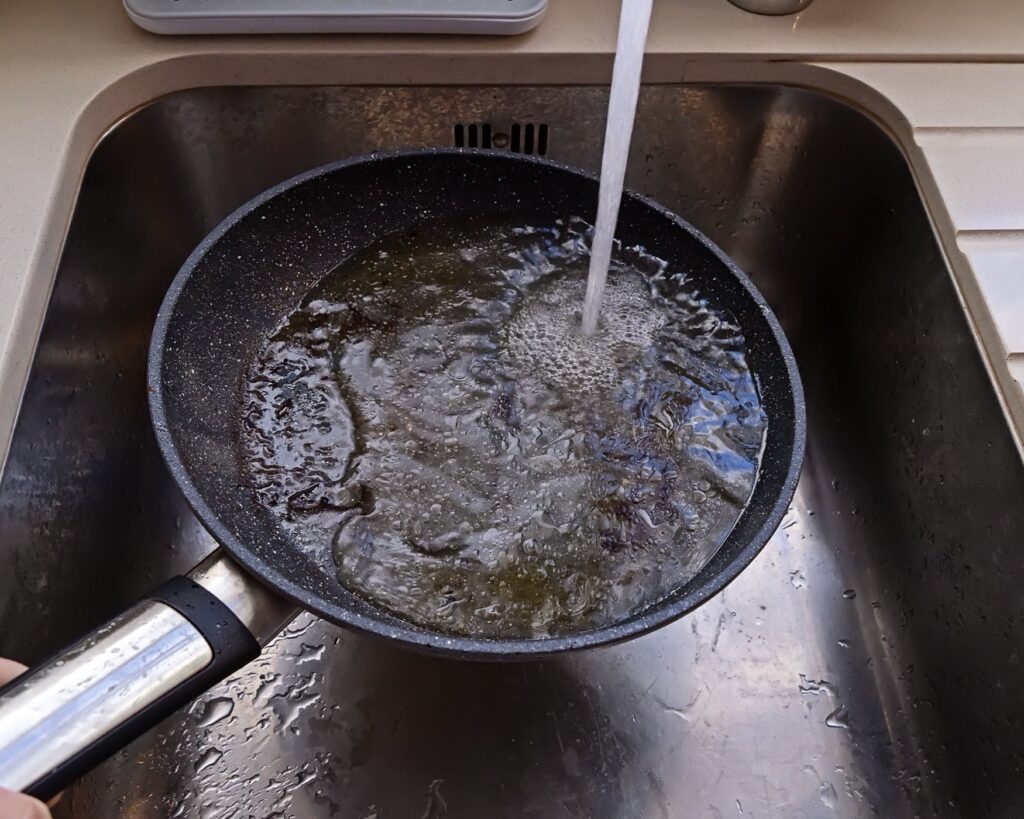

The belief that flushing grease down the drain with hot water can prevent blockages is a widespread myth that has been passed down through generations of homeowners. However, this practice is not a solution to grease disposal and can actually contribute to the problem. To illustrate why this method is ineffective, let’s consider a personal story that highlights the real-life implications of relying on hot water to deal with grease.
A Lesson Learned the Hard Way
Sarah, a homeowner who loved to cook, always followed her grandmother’s advice: “As long as you run hot water, you can pour grease down the sink.” Trusting in this wisdom, Sarah didn’t think twice about disposing of cooking oil and grease by washing it down the kitchen sink, believing the hot water would keep the grease in liquid form until it safely passed through her home’s plumbing system.
However, one winter morning, Sarah woke up to a kitchen sink that wouldn’t drain and a foul odor that seemed to emanate from the pipes. Confused and concerned, she called a plumber, who discovered a significant blockage in the pipes leading from her kitchen. The culprit? A solid mass of hardened grease that had accumulated over time.
The plumber explained that despite Sarah’s use of hot water, the grease didn’t travel far enough through the pipes before cooling and solidifying. The ground temperature surrounding the pipes, particularly during the colder months, ensured that the grease solidified well within her property’s plumbing system. This revelation was a wake-up call for Sarah, who realized that her trusted method of grease disposal was flawed.
Understanding the Science
The story of Sarah’s plumbing woes underscores the importance of understanding the science behind grease disposal. Grease solidification in home plumbing is inevitable due to the temperature difference between the hot grease and the cool pipes. While hot water may seem like it’s washing the grease away, it only transports the problem a few feet further down the line where the grease eventually cools and sticks to the pipes.
Shifting to Sustainable Practices
Sarah’s experience led her to change her grease disposal habits. She started allowing grease to cool and then scraping it into the trash, a simple yet effective method that prevents grease from entering the plumbing system in the first place. Sarah’s story is a powerful reminder of the need to question and update our practices based on a better understanding of household maintenance and environmental responsibility.
The myth of hot water as a grease disposal solution is just that—a myth. By sharing personal stories like Sarah’s, we can spread awareness about the proper ways to dispose of grease and protect our homes and the environment from the unintended consequences of common household practices.

Can I use detergents to break down grease before washing it down the drain? While detergents can emulsify grease, making it seem like it’s safe to wash down the drain, this is a temporary solution. The grease eventually separates from the detergent solution further down the sewer line, where it can solidify and cause blockages. The best practice is to avoid disposing of grease down the drain altogether.
What should I do with large amounts of cooking oil, like after frying? Large volumes of cooking oil should be cooled and then poured into a container, such as an old jar or a special grease disposal system, which can then be thrown away with the solid waste. Some communities offer recycling programs for cooking oil, which is then converted into biodiesel, a cleaner-burning alternative to traditional diesel.
Are there any environmentally friendly ways to dispose of grease? Yes, aside from recycling programs that convert cooking oil into biodiesel, small amounts of grease can be composted with caution. However, this typically applies to vegetable-based oils and should be done in moderation within a well-managed compost system to avoid attracting pests.
Does grease really cause that much damage to municipal sewer systems? Absolutely. Municipalities spend millions of dollars annually cleaning out sewers clogged with grease. These blockages can lead to sewage overflows into streets and natural water bodies, posing significant environmental and public health risks. By properly disposing of grease at home, residents can play a crucial part in reducing these costly and hazardous blockages.
If I’ve been pouring grease down the drain, what should I do to prevent future blockages? It’s never too late to start good habits. Begin disposing of grease properly by letting it solidify and scraping it into the trash. For existing buildup, consider using a bacterial drain cleaner that can naturally break down grease without damaging pipes. However, severe blockages may require professional cleaning to clear the pipes and restore proper drainage.
By addressing these common inquiries, our goal is to demystify the issue of grease disposal and encourage practices that safeguard both home plumbing systems and broader municipal sewer networks. Proper grease management is not just a matter of household maintenance; it’s a significant environmental responsibility that, when managed correctly, contributes to the health and wellbeing of entire communities.

Preventing Carbon Monoxide Dangers
The buildup of grease in plumbing can cause significant issues, much like how snow accumulation around exhaust vents can pose serious risks of carbon monoxide poisoning in homes. Just as we emphasize the importance of proper grease disposal to prevent blockages and environmental damage, it’s equally important to ensure that snow does not block heating equipment vents. A blocked vent can cause dangerous gases to accumulate inside your home, posing a lethal risk to inhabitants. The article “Winter Warning: Prevent Carbon Monoxide Danger by Clearing Snow” highlights the importance of regularly checking and clearing snow from around these vents to ensure that heating systems can operate safely and efficiently. This preventive measure is a simple yet vital step in safeguarding your household from the invisible threat of carbon monoxide.
Selecting and Troubleshooting Your Ideal Water Heater
Similarly, the choice and maintenance of your water heater have a direct impact on your home’s environmental footprint and safety. Just as disposing of grease correctly can prevent long-term damage to your home’s plumbing, selecting the right water heater can enhance energy efficiency and reduce unnecessary strain on resources. The guide “Heating It Up: Selecting and Troubleshooting Your Ideal Water Heater” offers valuable insights into choosing a water heater that meets your family’s needs while considering energy consumption and efficiency. It also provides troubleshooting tips for common issues, ensuring that your system runs smoothly and sustainably. Understanding your water heater’s operation and maintenance needs can help prevent unexpected breakdowns, ensuring reliable access to hot water for both cooking and cleaning—activities that contribute to the overall management of household waste, including grease.

The Connection Between Home Maintenance and Environmental Responsibility
Both the proper disposal of grease and the efficient management of home heating systems underscore a broader theme of environmental responsibility and safety in household maintenance. Whether it’s ensuring that grease doesn’t clog our pipes or that our homes remain safe and warm during winter months, each action we take contributes to a safer, more sustainable living environment. By adopting practices that protect our plumbing and heating systems, we not only safeguard our homes from immediate dangers but also contribute to the well-being of our communities and the environment at large.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases through some links in our articles.



